Cardiac arrest
 We talk about cardiac arrest when the heart is no longer able to keep the circulation going due to it pumping inadequately. The blood flow stops. It can no longer be guaranteed that the brain and other organs will be supplied with oxygenated blood.
We talk about cardiac arrest when the heart is no longer able to keep the circulation going due to it pumping inadequately. The blood flow stops. It can no longer be guaranteed that the brain and other organs will be supplied with oxygenated blood.
Symptoms are
- Unconsciousness
- No longer breathing and no circulation (no vital signs)
First Aid means here
- Realise: Cardiac arrest: every second counts!
- Alarm: Immediately raise internal (first aiders, AED) and external alarm (emergency number 144)!
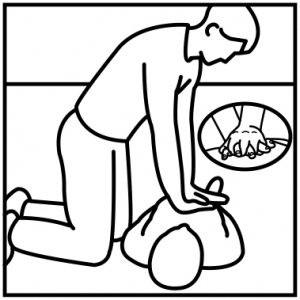
- Pump: Immediately start chest compressions!
- Shock: First defibrillation within 3 minutes!
- Consider Artificial respiration using pocket mask / aids
Please also note
With cardiac arrest literally every second counts. 75 percent of those affected survive with defibrillation within 3 minutes, significantly more / less with better / worse response times. Chest compressions must be started straight away and should only be interrupted for analysis and shocking using the AED. Artificial respiration should be started as soon as you have assessed the situation, raised the alarm, started compressions and shocked, as soon as there are enough first aiders available and / or the conditions are in place so that chest compressions and the use of the AED are not restricted despite artificial respiration attempts.








